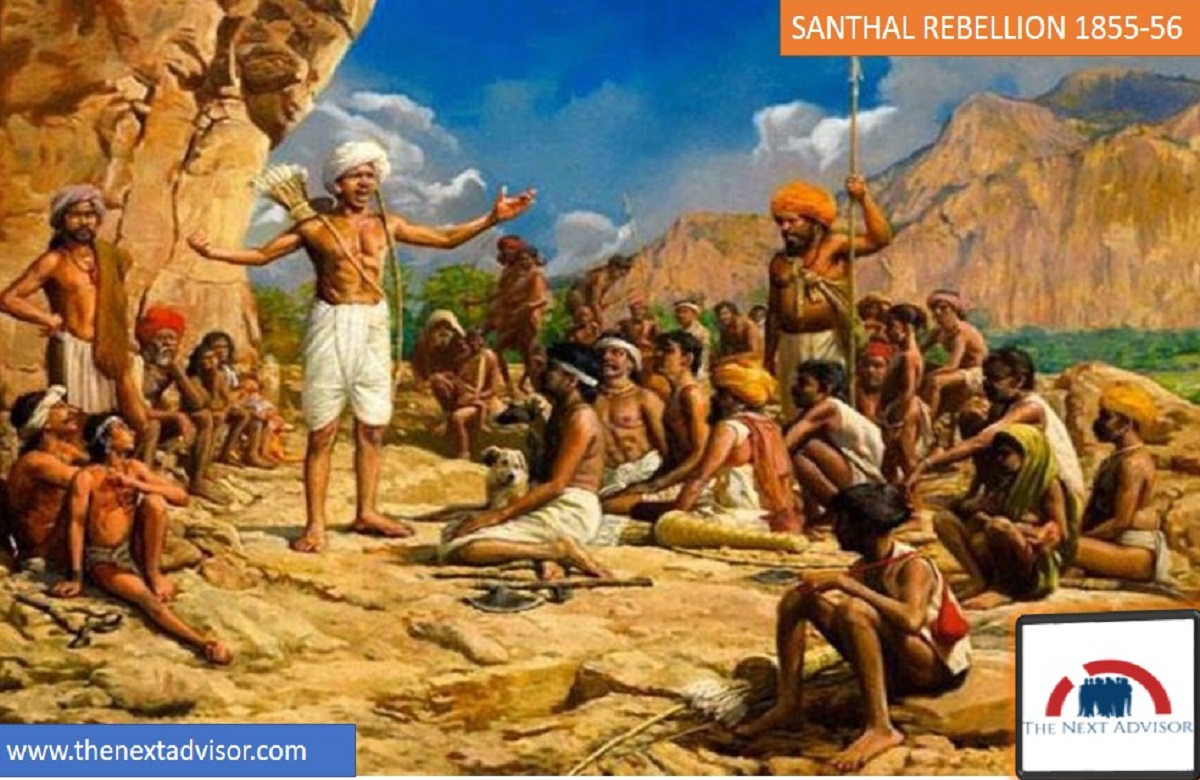
Introduction, Friends let’s see about the SANTHAL REBELLION 1855-56.
Peasant revolts of the 18th and 19th centuries have played an important role in Indian independence. Santhal Rebellion is one such revolt against the oppression of Santhals ( agricultural people) settled in Rajmahal Hills in Bihar.
Who were the Santhals? what is the SANTHAL REBELLION 1855-56?
They were the agricultural people settled in the Rajmahal Hills of Bihar. British turned to them for the expansion of the revenue through agriculture. Santhals agreed to clear forests to practice settled agriculture. In 1832, a large number of areas were demarcated as Damin-i-Koh or santal pargana. However, gradually the exploitation started from the British side and to such an extent, that it gave rise to Santhal Rebellion.
Important Facts of SANTHAL REBELLION 1855-56
The Santhals are the largest tribal group in India today, per the population figures. They are native to the Indian state of predominantly Jharkhand. West Bengal and Odisha.
Until the 19th century, they lived their lives in harmony with nature and practiced shifting agriculture and hunting. They lived in the hilly regions of Birbhum, Barabhum, Manbhum, Palamau, and Chhotanagpur.
These areas came under the Bengal Presidency those rule by the British after the battle of Plassey in 1757. The Santhal life was disrupted by the onslaught of the Zamindari system that they introduced. They were rendered landless bonded laborers in their own homes.
The local landlords occupy the Santhal lands and exploited them.
The tribals engaged in commercial activity through the barter system. When currency was introduced because of the colony’s intervention, The Santhals were fierce but they were honorable, According to some British observers of the time, the Santhals used poisoned arrows for hunting but did not use poisoned arrows against their enemies in war. Ironically, the British came to ‘mobilize’ the natives.
Martial law was declared on 10th November 1855 and it lasted till 3rd January 1856.
The British passed the Santhal progenies Tenancy Act in 1876 which offered some protection for the tribals against exploitation.
The Santhal rebellion was overshadowed by the revolt of 1876 but it remains a watershed in the evolution of the modern Santhali identity. it played an important role in the creation of the state of Jharkhand in 200